
Our planetary system is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy.
Our solar system consists of our star, the Sun, and everything bound to it by gravity — the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, dwarf planets such as Pluto, dozens of moons and millions of asteroids, comets and meteoroids. Beyond our own solar system, we have discovered thousands of planetary systems orbiting other stars in the Milky Way.
Our solar system is made up of a star, eight planets and countless smaller bodies such as dwarf planets, asteroids and comets.
Our solar system orbits the center of the Milky Way Galaxy at about 515,000 mph (828,000 kph). We’re in one of the galaxy’s four spiral arms.
It takes our solar system about 230 million years to complete one orbit around the galactic center.
There are three general kinds of galaxies: elliptical, spiral and irregular. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy.
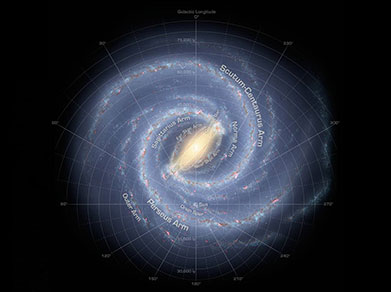
There are three general kinds of galaxies: elliptical, spiral and irregular. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy.
Our solar system is a region of space. It has no atmosphere. But it contains many worlds—including Earth—with many kinds of atmospheres.
The planets of our solar system—and even some asteroids—hold more than 150 moons in their orbits.
The planets of our solar system—and even some asteroids—hold more than 150 moons in their orbits.
The four giant planets—and at least one asteroid—have rings. None are as spectacular as Saturn’s gorgeous rings.
More than 300 robotic spacecraft have explored destinations beyond Earth orbit, including 24 astronauts who orbited the moon.
Our solar system is the only one known to support life. So far, we only know of life on Earth, but we’re looking for more everywhere we can.
NASA’s Voyager 1 is the only spacecraft so far to leave our solar system. Four other spacecraft will eventually hit interstellar space.

Five spacecraft have achieved enough velocity to eventually travel beyond the boundaries of our solar
system.
Two of them reached the unexplored space between the stars after several decades in space.
Voyager 1 went interstellar in
2012 and
Voyager 2 joined it in 2018. Both spacecraft
are still in
communication
with Earth. Both spacecraft launched in 1977.
NASA's New Horizons spacecraft—currently exploring the an icy region beyond Neptune
called
the
Kuiper
Belt—eventually will leave our solar system.
Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 also will ultimately travel silently among the
stars.
The
spacecraft used
up
their
power supplies decades ago.
Page Updated: October 7, 2019